HTTP vs HTTPS: A Comprehensive Guide
HTTP vs HTTPS: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
The internet, which links billions of users to websites and services every day, is the foundation of modern communication. Two essential protocols, HTTP and HTTPS, facilitate this data flow in the background. The increasing need for security and privacy has made HTTPS the preferred protocol, even though HTTP has long been the default for accessing web sites. The purpose of this blog is to examine these protocols, their distinctions, and the reasons that HTTPS is now required for a safer online experience.
What is HTTP?
The fundamental protocol that allows communication between a web browser and a web server is called HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It makes it easier for users to access websites and transfers data, including text, photos, and videos. However, HTTP operates in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access. While it’s effective for transferring non-sensitive information, it is not ideal for securing private data.
How Does HTTP Protocol Work?
The HTTP protocol operates according to the request-response approach:
Request: The web browser makes a request for particular resources (such as an image or web page) to the server.
Reaction: The requested resource is returned when the server has processed the request.
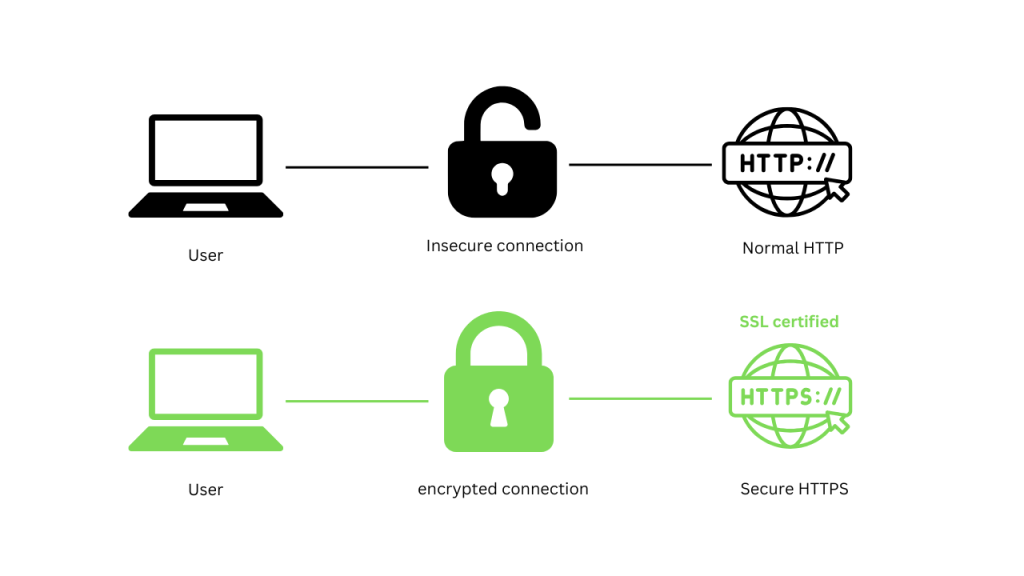
For example, when you type http://example.com in your browser, an HTTP request is sent to the server hosting that website, and the server responds by delivering the requested content. Any data sent can be intercepted by third parties because HTTP does not encrypt this transmission, rendering it vulnerable to cyberattacks.
What is HTTPS?
The secure variant of HTTP is called Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, or HTTPS. Sensitive data, such credit card numbers and passwords, is kept private by adding an extra layer of encryption to protect data while it is being transmitted. A secure channel of communication is established between the web browser and the server via HTTPS, which uses SSL/TLS encryption. Furthermore, by confirming the authenticity of websites, HTTPS assists users in recognizing trustworthy platforms and avoiding scams.
How Does HTTPS Protocol Work?
The following methods are used by HTTPS to improve HTTP:
Encryption: SSL/TLS encrypts data so that anyone intercepting the connection cannot read it.
Authentication: The server authenticates the website by presenting the browser with an SSL certificate.
Secure Communication: Data integrity and confidentiality are ensured by the secure connection that is established between the browser and server.
For example, visiting https://example.com ensures that all data transmitted between your browser and the website is encrypted and secure.
What’s the Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS?
Security is the primary difference between HTTP and HTTPS. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) adds an encryption layer utilizing SSL/TLS protocols to protect the data during transmission, whereas HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) delivers data in plain text, leaving it open to hacker interception. Any information sent, including payment information or login passwords, is safely secured using HTTPS to avoid unauthorized parties from seeing it. Apart from encryption, HTTPS also confirms the website’s legitimacy, ensuring that users are connecting to an authentic website. Because of this, HTTPS is not only more secure but also necessary to increase user trust and improve search engine ranks.
Why HTTPS is Essential for Security?
Protects Sensitive Data: HTTPS uses encryption to protect sensitive data, including credit card numbers, passwords, and personal information. This guarantees that during transmission, hackers or other scammers cannot access sensitive data.
Increases User Confidence: HTTPS enabled websites indicate a secure connection by displaying a padlock icon in the address bar of the browser. Users are encouraged to provide their information or complete transactions without concern because of this visual reassurance, which builds confidence.
Enhances SEO Rankings: Websites that support HTTPS are given preference by search engines like Google, which raises their ranking in search results. Websites that use HTTPS not only protect their connections but also improve their online exposure and effectiveness.
How HTTPS Requests and Responses Are Encrypted by TLS/SSL
TLS/SSL protects communication by using encryption to create a secure connection between the browser and the server. To authenticate the server and exchange a distinct session key, it combines public and private keys. All further information is encrypted by this session key, ensuring the privacy of queries and answers. Ensuring secure communication and protecting sensitive information, the data appears as an unintelligible string of characters even if it is intercepted.
Conclusion
It is now essential to switch from HTTP to HTTPS in order to maintain user confidence and online security. In addition to protecting sensitive data, HTTPS improves SEO ranks and complies with current security standards. Whether you manage a website or use the internet, switching to HTTPS is a crucial step in creating a safer online space.



